No.148 Yongda Road, Jiangkou Street, Huangyan, Taizhou, Zhejiang, China.
Material Selection and Design Considerations
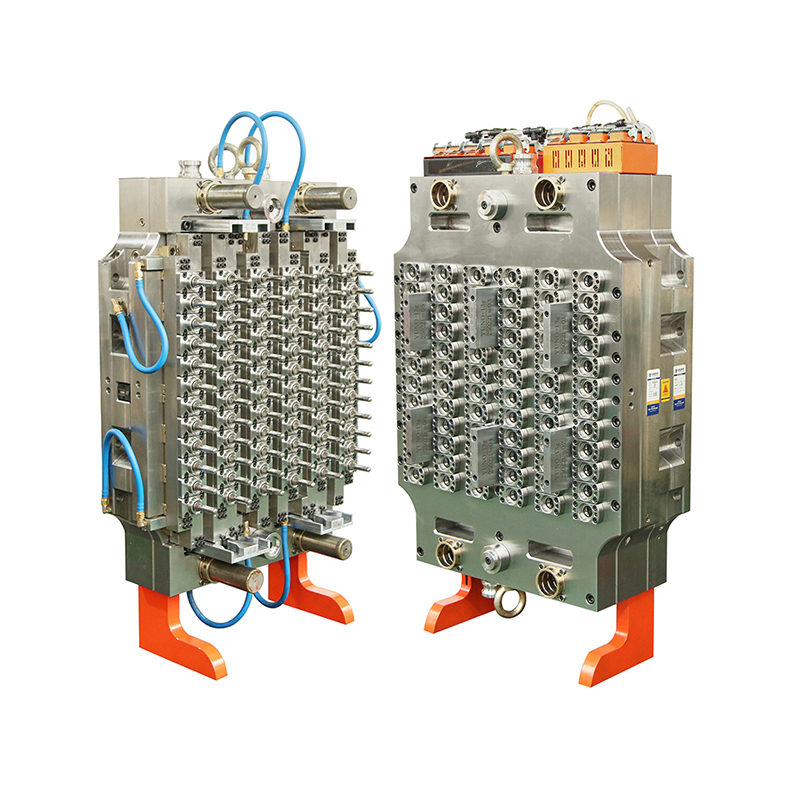
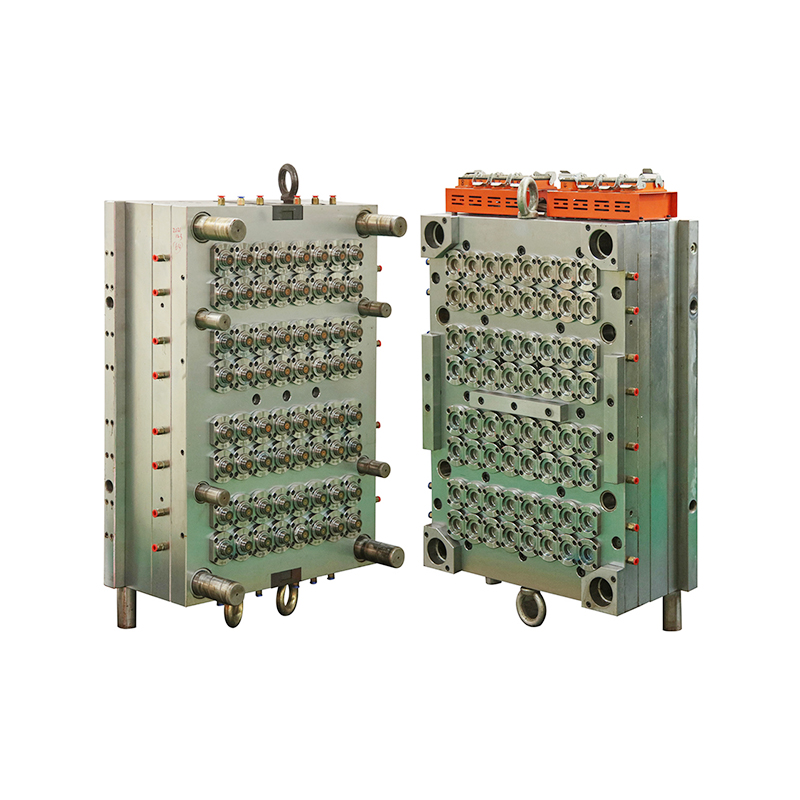
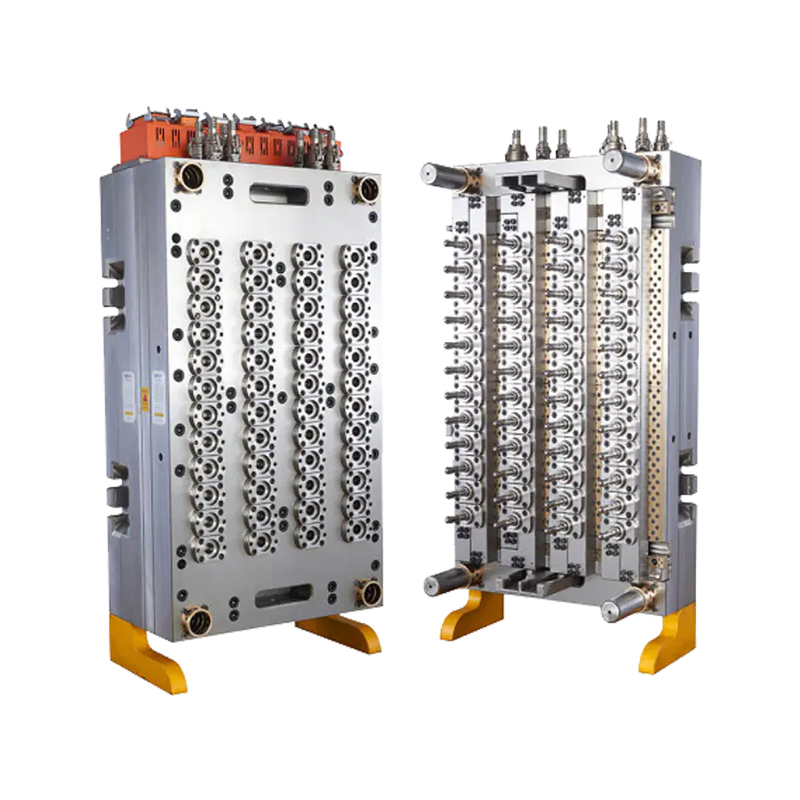
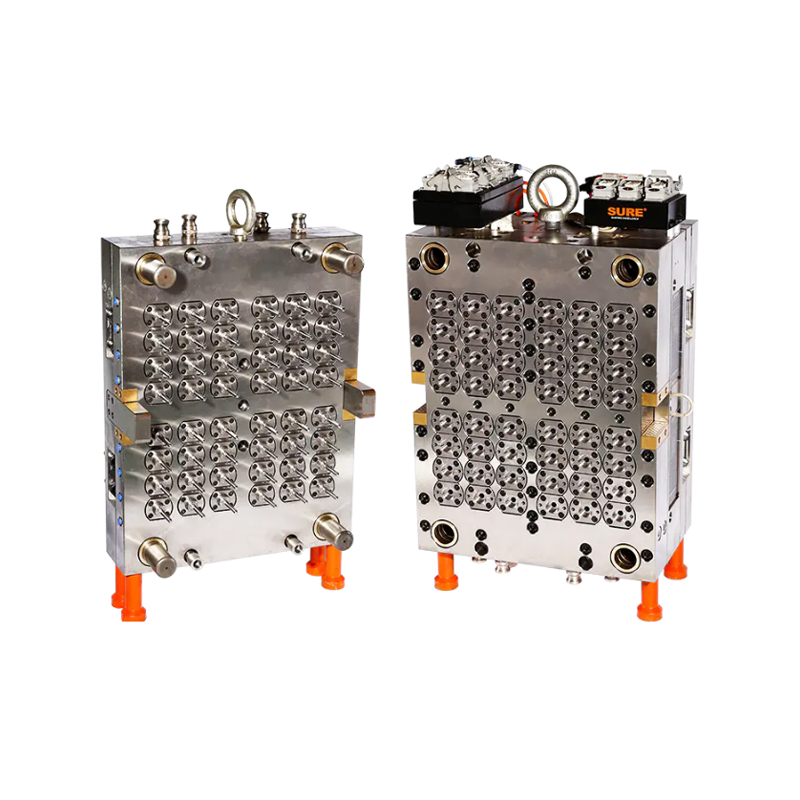
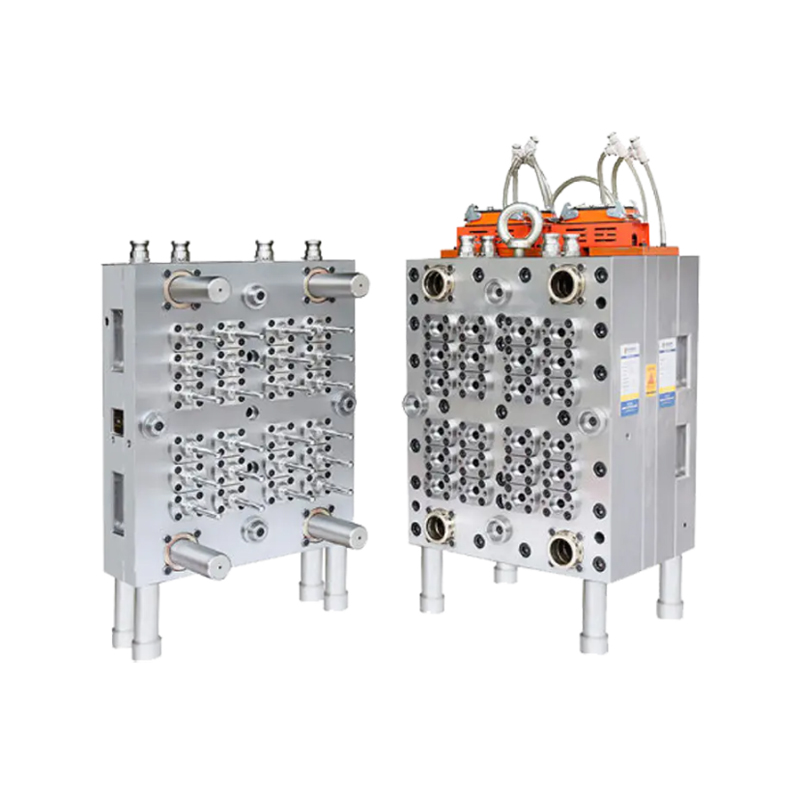
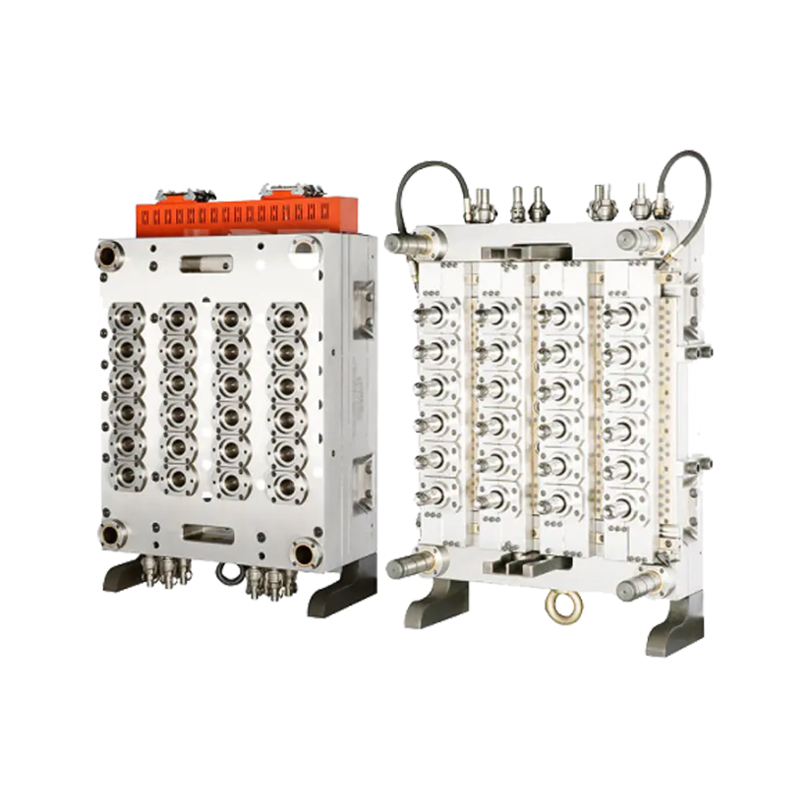
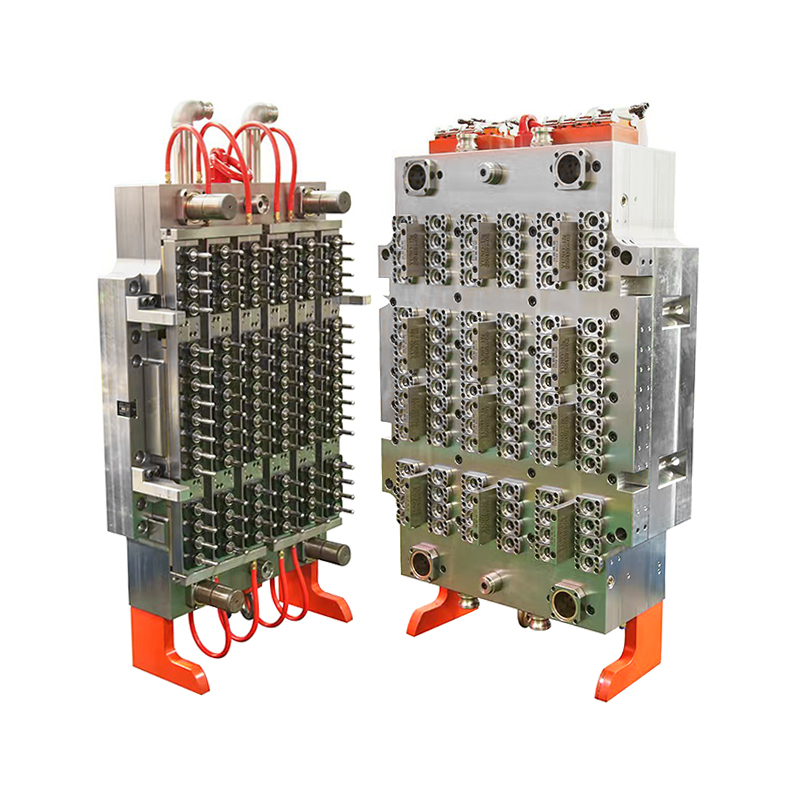
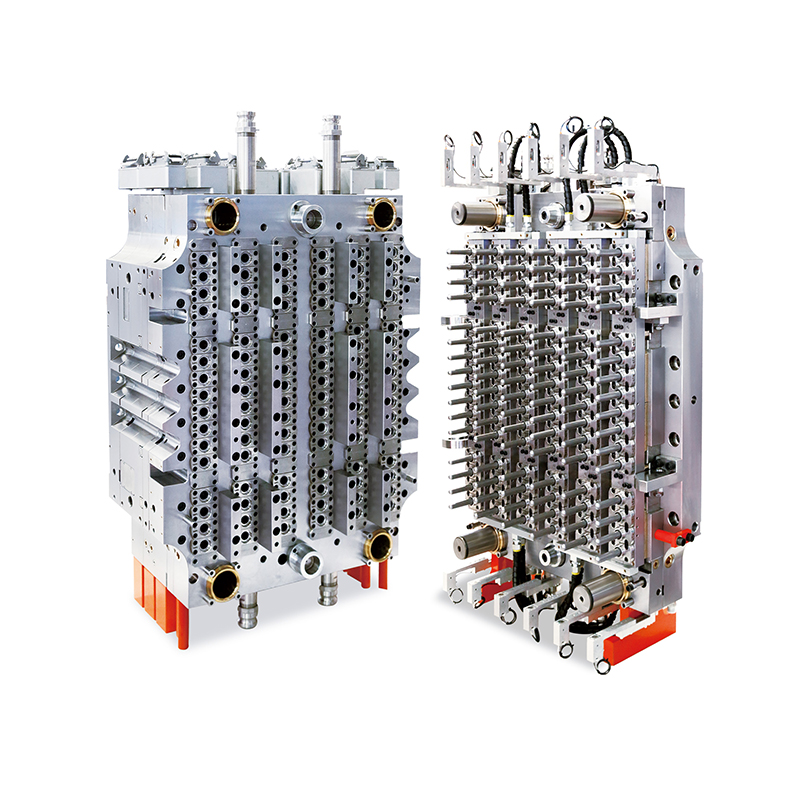
Medical moulds are essential for producing components used in medical devices, instruments, and packaging. High-quality steel, aluminum, and specialty alloys are commonly used to ensure durability, precision, and resistance to wear. The choice of material depends on the medical application, required tolerances, and production volume. Materials must maintain structural integrity and surface finish to meet strict industry standards.
Designing medical moulds requires careful consideration of accuracy, repeatability, and functionality. Every cavity, channel, and angle must be engineered to produce parts that fit perfectly in medical assemblies or devices. Complex designs, such as surgical instrument handles or injection moulded packaging, rely on the accuracy and reliability of the mould to function correctly.
Manufacturing Techniques and Precision
The production of medical moulds involves advanced machining techniques, including CNC milling, EDM (electrical discharge machining), and polishing. Precision is critical, as even small deviations can compromise the safety or effectiveness of medical devices. Surface finishing is also essential, as smooth or textured surfaces may be required depending on the application. Polished surfaces prevent bacterial growth and support sterilization processes, while textured surfaces improve grip or functionality in medical instruments.
Moulds are often tested using sample runs to verify dimensional accuracy, surface quality, and fit. Adjustments are made if necessary to ensure that each mould produces components that meet strict medical standards. The manufacturing process emphasizes repeatability, allowing consistent production of parts across multiple cycles. Reliable and accurate medical moulds contribute directly to the safety and usability of medical devices.
Applications in the Medical Industry
Medical moulds are used in a variety of applications, including surgical instruments, diagnostic tools, medical packaging, and laboratory equipment. Injection-moulded syringes, caps, and containers rely on precise moulds to maintain proper dimensions and functionality. Components such as instrument handles or connectors must adhere to strict ergonomic and safety requirements. The quality of the mould directly affects the reliability of medical devices, making precision and durability critical.
Customisation is common in medical mould production, as different hospitals or manufacturers require parts with unique dimensions, features, or branding. Moulds can be designed to produce specialized components for single-use applications, reusable instruments, or protective packaging. Advanced moulding techniques support the production of complex geometries, thin walls, and multi-component assemblies, meeting the diverse needs of the healthcare industry.
Efficiency and Quality Assurance
Medical mould production emphasizes efficiency without compromising quality. Automated production lines use moulds for injection, compression, or blow moulding processes to achieve consistent output. Regular maintenance and inspection ensure that moulds remain accurate over repeated cycles. Quality control includes dimensional checks, surface inspections, and verification of material properties. Engineers often monitor temperature, pressure, and cycle times during production, making small adjustments when necessary to maintain precision. Detailed documentation of each batch helps track performance and quickly identify any inconsistencies.
Medical moulds help manufacturers produce safe, reliable, and functional medical components. Accurate moulds support both mass production and specialized applications, ensuring that medical devices perform effectively and meet regulatory requirements. Efficient mould production enables manufacturers to supply the healthcare industry with consistent, high-quality components. By combining meticulous design, careful monitoring, and structured quality assurance, manufacturers reduce errors, enhance consistency, and ensure that every part meets both functional and safety expectations.
 英语
英语 法语
法语